When it comes to building safety, fire system installation plays a massive role in protecting both people and property. Having a well-functioning fire protection system in place means that fires can be detected early, controlled, and, in many cases, fully suppressed before they become dangerous.
It doesn’t matter if you’re looking to install fire alarms, sprinklers, detection mechanisms, or fire suppression systems, each component requires thorough planning and regular upkeep.
Let’s break it all down into the basics—what’s involved, the steps for installation, and how to keep things running smoothly over time.
Table of Contents
ToggleDifferent Types of Fire Systems and Installation
Fire protection systems aren’t one-size-fits-all. Depending on the building’s purpose and layout, different fire systems may be required. Here’s a look at some of the most common types.
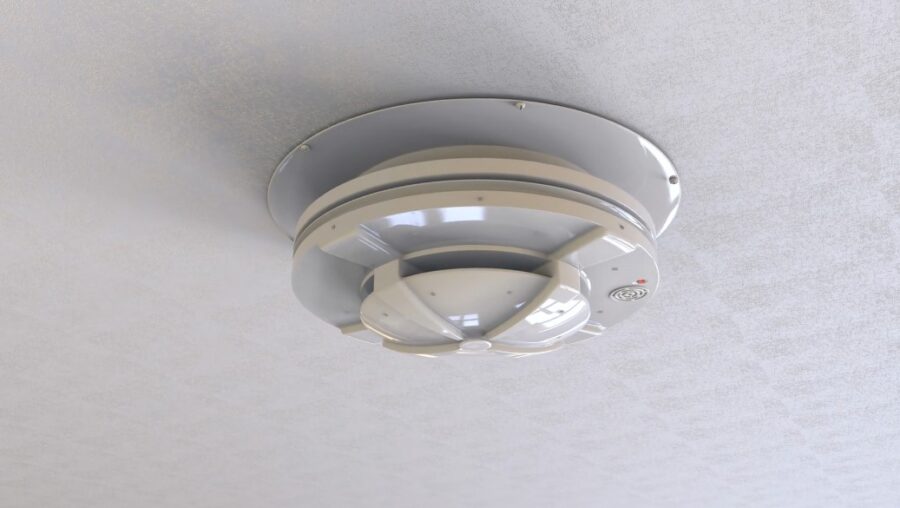
1. Fire Alarm Systems
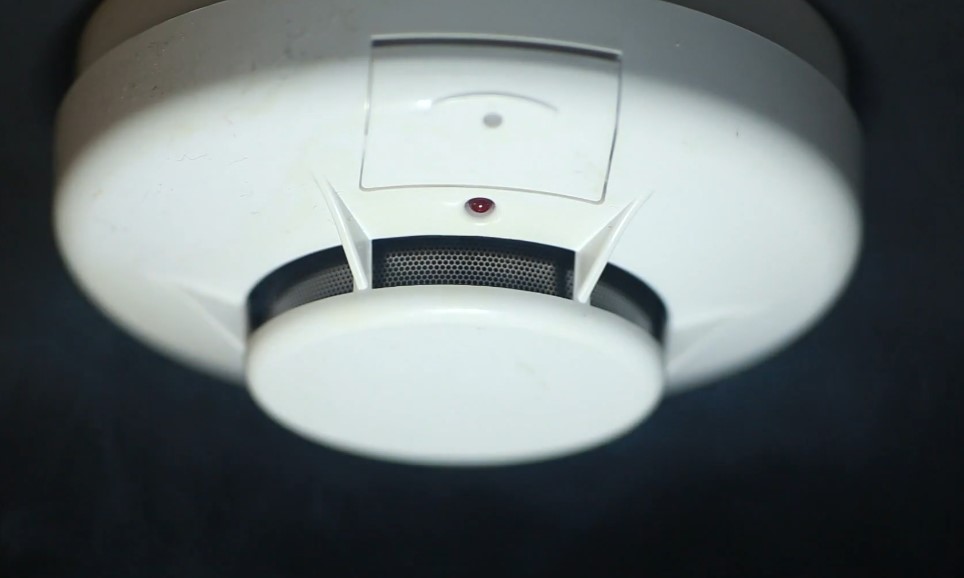

The main goal of a fire alarm system is simple: alert building occupants to get out when a fire starts. Fire alarms are a fundamental part of any fire protection plan.
Key Components
- Smoke and Heat Detectors: Devices that detect the presence of smoke or an unusual rise in temperature.
- Manual Pull Stations: Enable individuals to trigger the alarm manually if they spot a fire before the detectors do.
- Alarm Sounders and Strobes: These create loud noise and bright lights to alert everyone that it’s time to evacuate.
- Control Panels: The brain of the system, receiving input from the detectors and signaling alarms.
How Fire Alarms Are Installed
Fire alarm installation is a multi-step process. First, the right system for the building is chosen, typically based on its size, layout, and function. Then, detectors are placed in key areas like hallways and high-risk zones such as kitchens. It is important to note that you have to avoid humidity at any cost.
Wiring gets routed back to the control panel, and, once everything is connected, the system is tested. A fire alarm installation only counts as successful if it activates immediately and correctly in an emergency.
2. Sprinkler Systems

When most people think of fire protection, sprinkler systems come to mind. These systems automatically release water when they detect heat, helping to contain and, ideally, extinguish fires before they spread.
Common Types of Sprinklers
- Wet Pipe Systems: Always filled with water, ready to discharge at a moment’s notice.
- Dry Pipe Systems: Filled with pressurized air until heat triggers the release of water.
- Pre-action Systems: Activated in stages, only releasing water when specific conditions are met.
Installing Sprinklers
Installation involves a careful look at the building’s layout. Sprinkler heads need to be placed in areas where fire risk is highest and where they can cover the most ground.
Pipes are installed throughout the building and linked to a water supply, ensuring the right water pressure. Post-installation testing is a critical step to make sure that all components are ready to perform under pressure, especially for dry pipe and pre-action systems, which are more complex.
3. Fire Detection Systems
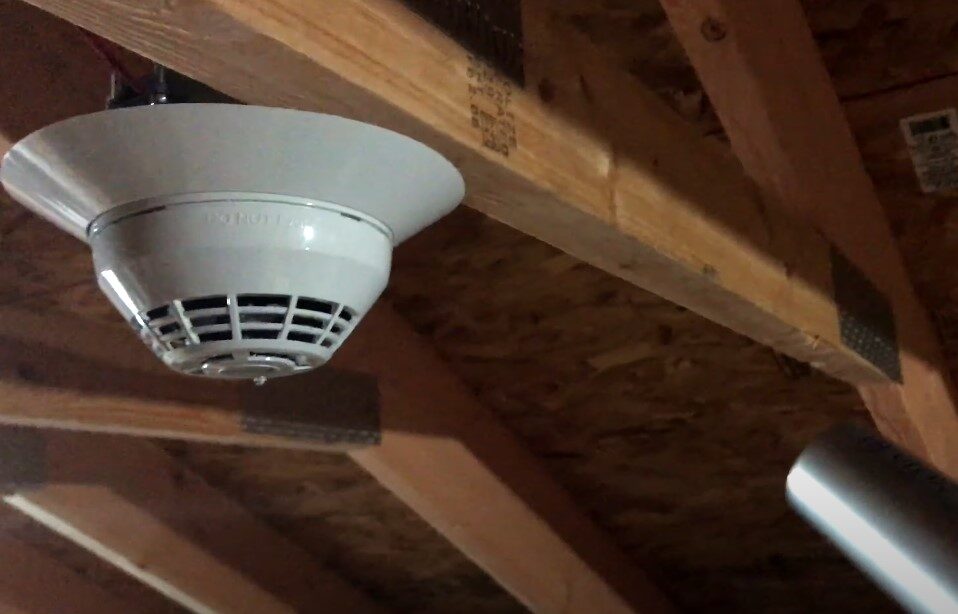

The sooner a fire is detected, the faster action can be taken. Fire detection systems serve as the frontline defense by identifying signs of trouble like smoke, heat, or even gas leaks.
Key Technologies
- Smoke Detectors: Detect smoke particles in the air.
- Heat Detectors: Trigger alarms based on sudden spikes in temperature.
- Gas Sensors: Identify the presence of dangerous gases that may indicate a fire or other hazard.
Placement and Considerations
Installing smoke detectors in kitchens, basements, and mechanical rooms is a must. But care is needed when setting the sensitivity.
Too sensitive, and you’ll get false alarms. Too lenient, and you might miss a critical warning.
4. Fire Suppression Systems
In certain buildings—think data centers, libraries, or labs—using water to fight a fire can cause more harm than good. That’s where fire suppression systems come in, utilizing alternative agents like gases, foams, or chemicals.
Types of Suppression Systems
- CO2 Systems: These displace oxygen to suffocate fires, making them effective in environments where water would cause damage.
- Clean Agent Systems: Chemicals like FM-200 and NOVEC 1230 are used to fight fires without harming sensitive electronics.
- Foam Systems: Particularly useful in areas where flammable liquids are stored, as foam helps prevent reignition.
Installation Process
Installing suppression systems requires precision. The room must be properly sealed to prevent leakage, and the system must be tied to fire alarms and detection systems for simultaneous activation during a fire event.
Key Considerations in Fire System Installation

Building Codes and Regulations
Fire system installations must adhere to local fire codes and standards to ensure safety. In the United States, the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) sets many of these guidelines.
Compliance with NFPA regulations isn’t just about following the law; it’s about making sure that your system will actually work when it matters most.
Local authorities can provide details on the specific requirements for different building types, so be sure to consult them during the planning stages.
System Design
Designing an effective fire protection system isn’t just about picking the right equipment. It’s about analyzing the building from top to bottom.
Is the building multi-story? Are there high-risk areas like kitchens or electrical rooms? What are the exit pathways? All of these factors play into how the system is designed.
For example, sprinklers shouldn’t block emergency exits, and alarms should be loud enough to be heard even in noisy environments.
Step-by-Step Installation Process
Installing a fire protection system involves several steps, each critical for ensuring a successful outcome.
Pre-installation Planning
Before any installation takes place, the building needs to be inspected thoroughly. During this stage, fire risks are assessed, and a tailored plan is created to fit within the building’s existing architecture.
This also includes mapping out the integration with other systems like HVAC and lighting.
Installation
Once the plan is in place, the actual installation process can begin. This involves running electrical wiring for alarms, laying pipes for sprinkler systems, and placing detectors where they’ll be most effective.
System Coordination
Fire systems need to work seamlessly with other building systems. HVAC systems, for instance, help manage smoke in the event of a fire, while emergency lighting ensures visibility during evacuations.
Final Testing
The last step is testing. Every part of the system must function exactly as planned, with alarms, sprinklers, and suppression agents activating correctly.
Maintenance and Testing
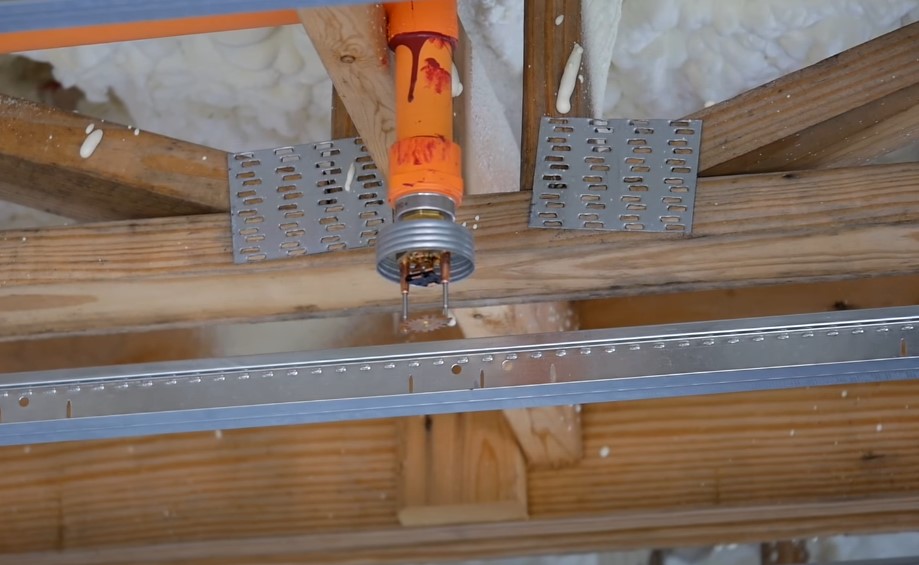

Once a fire protection system is in place, it’s not a “set it and forget it” situation. Regular maintenance is essential to keeping everything in working order.
Routine Maintenance Tasks
- Fire Alarm Testing: Monthly tests check that alarms are working and detectors are clean.
- Sprinkler System Inspections: Quarterly and annual inspections are needed to make sure the heads, pipes, and water pressure are all functioning properly.
- Suppression System Servicing: Gas and clean agent systems require monitoring to ensure there are no leaks and that suppression agent levels are maintained.
Sticking to a maintenance schedule is crucial. Systems that aren’t maintained properly may fail in an emergency, leaving building occupants at risk.
Costs of Installing a Fire System
Fire system installation costs can vary widely depending on the building’s size and the type of system needed. For example:
- A basic fire alarm system for a small office could range between $4,000 to $8,000.
- Larger buildings, especially those requiring integrated systems, will see costs rise significantly.
- Specialized fire suppression systems for environments like data centers may add even more to the total due to the use of complex and expensive suppression agents.
While fire system installations may seem costly upfront, it’s important to remember that investing in a quality system can save lives—and potentially reduce insurance premiums for your building.
Advancements In Fire Protection Technology
Technology is changing fire safety in exciting ways. For example:
- Smart Fire Alarms: These systems can send alerts directly to smartphones, enabling quick responses from building managers or owners.
- Integrated Building Management Systems (BMS): Fire systems are increasingly being integrated into broader building management systems, allowing centralized control of fire safety, security, HVAC, and lighting. Similarly, CCTV cameras are also increasing in popularity.
- Eco-friendly Suppression Agents: New environmentally safe suppression agents are gaining traction, especially in commercial and industrial settings.
Final Thoughts
Installing a fire protection system isn’t just about compliance; it’s about safety. From alarms to sprinklers to suppression agents, each element plays a crucial role in keeping people and property safe. Remember, if, in any case, fire protection fails you, break the glass and get out. Your safety is what matters the most.
By planning carefully, following local codes, and staying on top of maintenance, you can ensure your system is ready to act when it’s needed most. Fires are unpredictable, but your fire protection system doesn’t have to be. Keep it prepared, and it’ll be there to protect when it counts.
Related Posts:
- PASS Method Fire Extinguisher - How It Can Save Lives
- Commercial Fire Alarm System - What You Need to Know
- What Is One Way a Command Economy Affects the Lives…
- NYC Squatters Rights in 2025 - Must-Read for Property Owners
- Why the U.S. Must Do More to Protect Migrants’ Human Rights
- How to Legally Protect Yourself When Buying…